What are the symptoms?

A deeper look: Muscle tone, stretch reflex and spasticity
In simple terms, spasticity is increased resistance to passive movement and is caused by prolonged muscle contraction. Muscle tone is a state of tension that is maintained continuously, even when a person is relaxed, and which increases in resistance to passive stretch.
It helps to maintain posture and decreases during sleep. The stretch reflex is a muscle contraction in response to stretching within the muscle. This reflex, by definition extremely fast, exists to allow the muscle to adapt to any kind of muscular tone and change to avoid over-stretching.
In spasticity, the muscle tone is abnormally increased (muscle hypertonia) and reflexes, such as the stretch reflex, may persist for too long and may be too strong (hyperactive reflexes). These phenomena cause an increased resistance to passive movement (e.g. if someone else tries to move the extremities of the person affected).
Spasticity can range from very mild to debilitating and painful. The main symptoms are:
Symptoms of spasticity
Spasticity can range from very mild to debilitating and painful. The main symptoms are:


How does spasticity affect different parts of the body?
Spasticity symptoms can occur in the upper and/or the lower limbs. The extent of spasticity and areas of the body affected depends on the area of the brain or spinal cord that has been damaged.
There are four types of spasticity: Hemiplegia, Hemiparesis, Diplegia and Quadriplegia.


Hemiplegia / Hemiparesis
- In spastic hemiplegia, the muscles of one side of the body are affected, resulting in constant contraction of the muscles, severe or complete loss of strength and paralysis of one side of the body. Generally, injury to the left side of the brain will cause symptoms in the right side of the body, and vice versa.
- In spastic hemiparesis, muscles on one side of the body are abnormally stiff and there is weakness on one side of the body. Patients affected can still move the impaired side of their body but with reduced muscular strength. This can be associated with other deficits such as a decrease in sensitivity and/or a decrease of body part position perception. Hemiplegia is more severe and defined as total absence of controlled movement.


Diplegia
- In spastic diplegia, the lower limbs are most often affected, and the term used is paraplegia. These cases are mainly related to a lesion of the spinal cord. Diplegia rarely concerns the two upper limbs.


Quadriplegia
- All four limbs are affected in patients with spastic quadriplegia. This is mainly related to a lesion of the spinal cord.
Upper limb spasticity
While spasticity may affect any muscle group, it often produces stereotypical patterns in posture. Spasticity frequently affects muscles that work against the force of gravity. In other words, upper limb spasticity tends to affect the flexors (biceps, brachialis and brachioradialis) of the arm.
When a patient suffers from spasticity, these patterns can all affect your motor ability when performing simple everyday tasks such as dressing, eating or grasping, and may also interfere with balance, causing mobility difficulties.
Common clinical patterns of upper limb spasticity include:





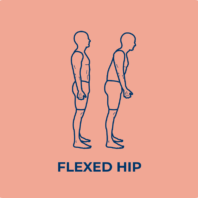
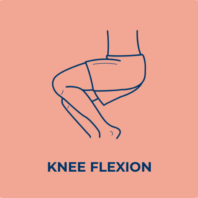
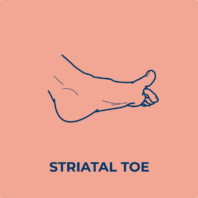
Lower limb spasticity
Spasticity often produces stereotypical patterns in posture, depending on the muscles affected by increased muscle tone.
Spasticity frequently affects muscles that work against the force of gravity. In other words, in the leg, it tends to affect the extensors.
Common clinical patterns of lower limb spasticity include:



Which rehabilitation devices do you need?
Find out more about the wide array of rehabilitation devices offered to make life easier and help regain some independence when living with spasticity.

Tips & tricks
When did you notice the first symptoms of PSS after your stroke?
Find out more about available tips and tricks that make daily life challenges easier to cope with for spasticity patients.
Exercises on the trick board – exercises to do at home.
There are a number of exercises that can be done at home to improve mobility or reduce acute spasticity.
What do you use for strengthening your hand?
Many tips and tricks are designed to be executed with one hand, making it possible to complete activities that can otherwise only be attempted with two hands.


